#javascript basic data structures
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Introduction to JavaScript for Beginners: Unlock the Power of Web Development 2023
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on JavaScript for beginners. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of JavaScript, one of the most versatile and widely-used programming languages on the web. Whether you’re an aspiring web developer or simply curious about the fascinating realm of coding, we’ve got you covered. Let’s embark on this exciting journey and unlock the potential of…

View On WordPress
#Back-end#Beginners Guide#Coding Essentials#Control Structures#Data Types#Dynamic Web Pages#Events#Front-end#Functions#Interactive Web#JavaScript#JS Basics#Learning JavaScript#Loops#Modern Web Development#programming#Text Editors#Variables#Web Applications#Web Browsers#web development
0 notes
Text
A structured way to learn JavaScript.
I came across a post on Twitter that I thought would be helpful to share with those who are struggling to find a structured way to learn Javascript on their own. Personally, I wish I had access to this information when I first started learning in January. However, I am grateful for my learning journey so far, as I have covered most topics, albeit in a less structured manner.
N/B: Not everyone learns in the same way; it's important to find what works for you. This is a guide, not a rulebook.
EASY
What is JavaScript and its role in web development?
Brief history and evolution of JavaScript.
Basic syntax and structure of JavaScript code.
Understanding variables, constants, and their declaration.
Data types: numbers, strings, boolean, and null/undefined.
Arithmetic, assignment, comparison, and logical operators.
Combining operators to create expressions.
Conditional statements (if, else if, else) for decision making.
Loops (for, while) for repetitive tasks. - Switch statements for multiple conditional cases.
MEDIUM
Defining functions, including parameters and return values.
Function scope, closures, and their practical applications.
Creating and manipulating arrays.
Working with objects, properties, and methods.
Iterating through arrays and objects.Understanding the Document Object Model (DOM).
Selecting and modifying HTML elements with JavaScript.Handling events (click, submit, etc.) with event listeners.
Using try-catch blocks to handle exceptions.
Common error types and debugging techniques.
HARD
Callback functions and their limitations.
Dealing with asynchronous operations, such as AJAX requests.
Promises for handling asynchronous operations.
Async/await for cleaner asynchronous code.
Arrow functions for concise function syntax.
Template literals for flexible string interpolation.
Destructuring for unpacking values from arrays and objects.
Spread/rest operators.
Design Patterns.
Writing unit tests with testing frameworks.
Code optimization techniques.
That's it I guess!
872 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hacktivism: Digital Rebellion for a New Age 🌐💥
In an era where our lives are intertwined with the digital landscape, the concept of hacktivism has become more than just a buzzword. It’s the fusion of hacking and activism—where people use their coding and cyber skills to disrupt power structures, challenge injustice, and amplify voices that often go unheard. It's a rebellion born from the belief that access to information, privacy, and freedom are rights, not privileges. But how did this digital resistance movement come to be, and how can you get involved? Let’s dive into it. 💻⚡️
What Exactly Is Hacktivism? 🤖✨
At its core, hacktivism is activism with a digital twist. It’s about using technology and hacking tools to advance social, political, and environmental causes. The most common methods include:
DDoS Attacks (Distributed Denial of Service): Overloading a target’s website with too much traffic, essentially crashing it, to temporarily shut down an online service.
Website Defacement: Replacing a website’s homepage with a political message, often exposing corruption or unethical practices.
Data Leaks: Exposing hidden documents or sensitive information that reveal corporate or governmental wrongdoing.
Bypassing Censorship: Circumventing firewalls or government restrictions to make sure information reaches the people it needs to.
The idea is simple: when a government or corporation controls the narrative or hides the truth, hacktivists take it into their own hands to expose it. 🌍💡
Why Is Hacktivism Important? 🔥
In a world dominated by corporations and powerful governments, hacktivism represents a form of resistance that’s accessible. It’s about leveling the playing field, giving people—especially those who lack resources—an avenue to protest, to expose corruption, and to disrupt systems that perpetuate inequality. The digital world is where much of our lives now happen, and hacktivism uses the very systems that oppress us to fight back.
Think about WikiLeaks leaking documents that exposed global surveillance and the activities of intelligence agencies. Or how Anonymous has played a pivotal role in advocating for free speech, standing up against internet censorship, and exposing corrupt governments and corporations. These are the digital warriors fighting for a cause, using nothing but code and their knowledge of the web.
Hacktivism is a direct response to modern issues like surveillance, censorship, and misinformation. It's a way to shift power back to the people, to give voice to the voiceless, and to challenge oppressive systems that don’t always play by the rules.
The Ethical Dilemma 🤔💭
Let’s be real: hacktivism doesn’t come without its ethical dilemmas. While the intentions are often noble, the methods used—hacking into private systems, defacing websites, leaking sensitive info—can sometimes lead to unintended consequences. The line between activism and cybercrime is thin, and depending on where you live, you might face serious legal repercussions for participating in hacktivist activities.
It’s important to consider the ethics behind the actions. Are you defending the free flow of information? Or are you inadvertently causing harm to innocent bystanders? Are the people you’re exposing truly deserving of scrutiny, or are you just participating in chaos for the sake of it?
So if you’re thinking of getting involved, it’s crucial to ask yourself: What am I fighting for? And is the harm done justified by the greater good?
How to Get Started 💻💡
So, you’re interested in getting involved? Here’s a starting point to help you use your tech skills for good:
Learn the Basics of Hacking 🔐: Before diving into the world of hacktivism, you'll need to understand the tools of the trade. Start with the basics: programming languages like Python, HTML, and JavaScript are good foundational skills. Learn how networks work and how to exploit vulnerabilities in websites and servers. There are plenty of free online resources like Codecademy, Hack This Site, and OverTheWire to help you get started.
Understand the Ethical Implications ⚖️: Hacktivism is, above all, about fighting for justice and transparency. But it’s crucial to think through your actions. What’s the bigger picture? What are you trying to achieve? Keep up with the latest issues surrounding privacy, data rights, and digital freedom. Some online groups like The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) provide great resources on the ethics of hacking and digital activism.
Join Communities 🕸️: Being part of a like-minded group can give you support and insight. Online communities, like those on Reddit, Discord, or specific forums like 4chan (if you're cautious of the chaos), can help you learn more about hacktivism. Anonymous has also had an iconic role in digital activism and can be a place where people learn to organize for change.
Stay Informed 🌐: To be effective as a hacktivist, you need to be in the know. Follow independent news sources, activist blogs, and websites that report on global surveillance, corporate corruption, and governmental abuse of power. Hacktivism often reacts to injustices that would otherwise go unnoticed—being informed helps you take action when necessary.
Respect the Digital Space 🌱: While hacktivism can be used to disrupt, it’s important to respect the privacy and safety of ordinary people. Try to avoid unnecessary damage to private citizens, and focus on the systems that need disrupting. The internet is a tool that should be used to liberate, not to destroy without purpose.
Never Forget the Human Side ❤️: As with all activism, the heart of hacktivism is about making a difference in real people’s lives. Whether it's freeing information that has been hidden, protecting human rights, or challenging unjust power structures—always remember that at the end of the code, there are humans behind the cause.
Final Thoughts ��
Hacktivism is a powerful, transformative form of resistance. It’s not always about flashy headlines or viral attacks—often, it’s the quiet work of exposing truths and giving people a voice in a world that tries to keep them silent. It’s messy, it’s complex, and it’s not for everyone. But if you’re interested in hacking for a purpose greater than yourself, learning the craft with the intention to fight for a better, more just world is something that can actually make a difference.
Remember: With great code comes great responsibility. ✊🌐💻
#Hacktivism#DigitalRevolution#TechForGood#Activism#CodeForJustice#ChangeTheSystem#Anarchism#Revolution
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
Any tips on learning python? I already know Java, C++, and JavaScript.
Hiya! 💗
Since you already know those other languages, Python will be literally a piece of cake. It'll be easy for you, in my opinion.
Tips? I would say:
Start with the Basics: Begin by understanding the fundamental syntax and concepts of Python. After learning those, you can basically apply the languages you know logic into Python code and you'll be done. You can use online tutorials on YouTube or free online pdf books to get a good grasp of the basics.
Leverage Your Programming Experience:Like I mentioned Python shares similarities with many languages, so relate Python concepts to what you already know. For example, understand Python data types and structures in comparison to those in Java, C++, or JavaScript.
Projects and Practice:I sing this on my blog but practice is crucial. Start small projects or challenges to apply your Python knowledge. Depends what you want to build e.g. console apps, games, websites etc. Just build something small every so often!
Hope this helps! More tips I made: ask 1 | project ideas | random resources

⤷ ♡ my shop ○ my mini website ○ pinned ○ navigation ♡
#my asks#codeblr#coding#progblr#programming#studying#studyblr#learn to code#comp sci#tech#programmer#python#resources#python resources
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Normally I just post about movies but I'm a software engineer by trade so I've got opinions on programming too.
Apparently it's a month of code or something because my dash is filled with people trying to learn Python. And that's great, because Python is a good language with a lot of support and job opportunities. I've just got some scattered thoughts that I thought I'd write down.
Python abstracts a number of useful concepts. It makes it easier to use, but it also means that if you don't understand the concepts then things might go wrong in ways you didn't expect. Memory management and pointer logic is so damn annoying, but you need to understand them. I learned these concepts by learning C++, hopefully there's an easier way these days.
Data structures and algorithms are the bread and butter of any real work (and they're pretty much all that come up in interviews) and they're language agnostic. If you don't know how to traverse a linked list, how to use recursion, what a hash map is for, etc. then you don't really know how to program. You'll pretty much never need to implement any of them from scratch, but you should know when to use them; think of them like building blocks in a Lego set.
Learning a new language is a hell of a lot easier after your first one. Going from Python to Java is mostly just syntax differences. Even "harder" languages like C++ mostly just mean more boilerplate while doing the same things. Learning a new spoken language in is hard, but learning a new programming language is generally closer to learning some new slang or a new accent. Lists in Python are called Vectors in C++, just like how french fries are called chips in London. If you know all the underlying concepts that are common to most programming languages then it's not a huge jump to a new one, at least if you're only doing all the most common stuff. (You will get tripped up by some of the minor differences though. Popping an item off of a stack in Python returns the element, but in Java it returns nothing. You have to read it with Top first. Definitely had a program fail due to that issue).
The above is not true for new paradigms. Python, C++ and Java are all iterative languages. You move to something functional like Haskell and you need a completely different way of thinking. Javascript (not in any way related to Java) has callbacks and I still don't quite have a good handle on them. Hardware languages like VHDL are all synchronous; every line of code in a program runs at the same time! That's a new way of thinking.
Python is stereotyped as a scripting language good only for glue programming or prototypes. It's excellent at those, but I've worked at a number of (successful) startups that all were Python on the backend. Python is robust enough and fast enough to be used for basically anything at this point, except maybe for embedded programming. If you do need the fastest speed possible then you can still drop in some raw C++ for the places you need it (one place I worked at had one very important piece of code in C++ because even milliseconds mattered there, but everything else was Python). The speed differences between Python and C++ are so much smaller these days that you only need them at the scale of the really big companies. It makes sense for Google to use C++ (and they use their own version of it to boot), but any company with less than 100 engineers is probably better off with Python in almost all cases. Honestly thought the best programming language is the one you like, and the one that you're good at.
Design patterns mostly don't matter. They really were only created to make up for language failures of C++; in the original design patterns book 17 of the 23 patterns were just core features of other contemporary languages like LISP. C++ was just really popular while also being kinda bad, so they were necessary. I don't think I've ever once thought about consciously using a design pattern since even before I graduated. Object oriented design is mostly in the same place. You'll use classes because it's a useful way to structure things but multiple inheritance and polymorphism and all the other terms you've learned really don't come into play too often and when they do you use the simplest possible form of them. Code should be simple and easy to understand so make it as simple as possible. As far as inheritance the most I'm willing to do is to have a class with abstract functions (i.e. classes where some functions are empty but are expected to be filled out by the child class) but even then there are usually good alternatives to this.
Related to the above: simple is best. Simple is elegant. If you solve a problem with 4000 lines of code using a bunch of esoteric data structures and language quirks, but someone else did it in 10 then I'll pick the 10. On the other hand a one liner function that requires a lot of unpacking, like a Python function with a bunch of nested lambdas, might be easier to read if you split it up a bit more. Time to read and understand the code is the most important metric, more important than runtime or memory use. You can optimize for the other two later if you have to, but simple has to prevail for the first pass otherwise it's going to be hard for other people to understand. In fact, it'll be hard for you to understand too when you come back to it 3 months later without any context.
Note that I've cut a few things for simplicity. For example: VHDL doesn't quite require every line to run at the same time, but it's still a major paradigm of the language that isn't present in most other languages.
Ok that was a lot to read. I guess I have more to say about programming than I thought. But the core ideas are: Python is pretty good, other languages don't need to be scary, learn your data structures and algorithms and above all keep your code simple and clean.
#programming#python#software engineering#java#java programming#c++#javascript#haskell#VHDL#hardware programming#embedded programming#month of code#design patterns#common lisp#google#data structures#algorithms#hash table#recursion#array#lists#vectors#vector#list#arrays#object oriented programming#functional programming#iterative programming#callbacks
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
JavaScript
Introduction to JavaScript Basics
JavaScript (JS) is one of the core technologies of the web, alongside HTML and CSS. It is a powerful, lightweight, and versatile scripting language that allows developers to create interactive and dynamic content on web pages. Whether you're a beginner or someone brushing up on their knowledge, understanding the basics of JavaScript is essential for modern web development.
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a client-side scripting language, meaning it is primarily executed in the user's web browser without needing a server. It's also used as a server-side language through platforms like Node.js. JavaScript enables developers to implement complex features such as real-time updates, interactive forms, and animations.
Key Features of JavaScript
Interactivity: JavaScript adds life to web pages by enabling interactivity, such as buttons, forms, and animations.
Versatility: It works on almost every platform and is compatible with most modern browsers.
Asynchronous Programming: JavaScript handles tasks like fetching data from servers without reloading a web page.
Extensive Libraries and Frameworks: Frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue make it even more powerful.
JavaScript Basics You Should Know
1. Variables
Variables store data that can be used and manipulated later. In JavaScript, there are three ways to declare variables:
var (old way, avoid using in modern JS)
let (block-scoped variable)
const (constant variable that cannot be reassigned)
Example:
javascript
Copy code
let name = "John"; // can be reassigned const age = 25; // cannot be reassigned
2. Data Types
JavaScript supports several data types:
String: Text data (e.g., "Hello, World!")
Number: Numeric values (e.g., 123, 3.14)
Boolean: True or false values (true, false)
Object: Complex data (e.g., { key: "value" })
Array: List of items (e.g., [1, 2, 3])
Undefined: A variable declared but not assigned a value
Null: Intentional absence of value
Example:
javascript
Copy code
let isLoggedIn = true; // Boolean let items = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"]; // Array
3. Functions
Functions are reusable blocks of code that perform a task.
Example:
javascript
Copy code
function greet(name) { return `Hello, ${name}!`; } console.log(greet("Alice")); // Output: Hello, Alice!
4. Control Structures
JavaScript supports conditions and loops to control program flow:
If-Else Statements:
javascript
Copy code
if (age > 18) { console.log("You are an adult."); } else { console.log("You are a minor."); }
Loops:
javascript
Copy code
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) { console.log(i); }
5. DOM Manipulation
JavaScript can interact with and modify the Document Object Model (DOM), which represents the structure of a web page.
Example:
javascript
Copy code
document.getElementById("btn").addEventListener("click", () => { alert("Button clicked!"); });
Visit 1
mysite
Conclusion
JavaScript is an essential skill for web developers. By mastering its basics, you can create dynamic and interactive websites that provide an excellent user experience. As you progress, you can explore advanced concepts like asynchronous programming, object-oriented design, and popular JavaScript frameworks. Keep practicing, and you'll unlock the true power of JavaScript!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diploma in Computer Application
A Diploma in Computer Application (DCA) is a popular short-term course that offers a solid foundation in computer fundamentals and applications. It's designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills to work in various IT-related roles.
Why Choose a DCA Course?
Quick and Efficient: DCA courses are typically shorter in duration, making it a time-effective way to acquire essential computer skills.
Practical Learning: The curriculum emphasizes hands-on training, allowing students to gain practical experience with software applications and hardware components.
Diverse Career Opportunities: A DCA certification opens doors to a wide range of job roles, including:
Data Entry Operator
Computer Operator
Web Designer
Software Tester
Technical Support Specialist
IT Assistant
Foundation for Further Studies: A DCA can serve as a stepping stone for higher education in computer science, information technology, or related fields.
Core Subjects in a DCA Course
Computer Fundamentals: Basic concepts of computers, hardware components, and software applications.
Operating Systems: Understanding and using various operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Microsoft Office Suite: Proficiency in MS Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook.
Internet and Web Technologies: Basics of the internet, web browsing, email, and web development tools like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Database Management Systems: Introduction to database concepts and SQL.
Programming Languages: Basic programming concepts in languages like C, C++, or Python.
How to Choose a Good DCA Institute
When selecting a DCA institute, consider the following factors:
Experienced Faculty: Ensure that the institute has experienced and knowledgeable faculty members.
Infrastructure: Well-equipped computer labs and other facilities are essential for practical learning.
Placement Assistance: A good institute should offer job placement assistance to help students secure employment.
Course Curriculum: The curriculum should be up-to-date and relevant to industry standards.
Fee Structure: Compare fees and financial aid options offered by different institutes.
By pursuing a Diploma in Computer Application, you can enhance your digital literacy, boost your career prospects, and stay relevant in the ever-evolving technological landscape.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
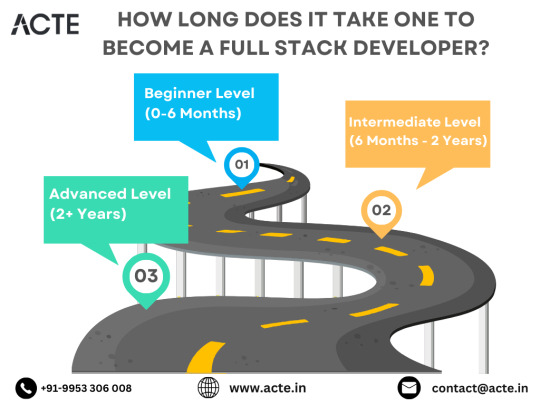
The Roadmap to Full Stack Developer Proficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
Embarking on the journey to becoming a full stack developer is an exhilarating endeavor filled with growth and challenges. Whether you're taking your first steps or seeking to elevate your skills, understanding the path ahead is crucial. In this detailed roadmap, we'll outline the stages of mastering full stack development, exploring essential milestones, competencies, and strategies to guide you through this enriching career journey.

Beginning the Journey: Novice Phase (0-6 Months)
As a novice, you're entering the realm of programming with a fresh perspective and eagerness to learn. This initial phase sets the groundwork for your progression as a full stack developer.
Grasping Programming Fundamentals:
Your journey commences with grasping the foundational elements of programming languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These are the cornerstone of web development and are essential for crafting dynamic and interactive web applications.
Familiarizing with Basic Data Structures and Algorithms:
To develop proficiency in programming, understanding fundamental data structures such as arrays, objects, and linked lists, along with algorithms like sorting and searching, is imperative. These concepts form the backbone of problem-solving in software development.
Exploring Essential Web Development Concepts:
During this phase, you'll delve into crucial web development concepts like client-server architecture, HTTP protocol, and the Document Object Model (DOM). Acquiring insights into the underlying mechanisms of web applications lays a strong foundation for tackling more intricate projects.
Advancing Forward: Intermediate Stage (6 Months - 2 Years)
As you progress beyond the basics, you'll transition into the intermediate stage, where you'll deepen your understanding and skills across various facets of full stack development.
Venturing into Backend Development:
In the intermediate stage, you'll venture into backend development, honing your proficiency in server-side languages like Node.js, Python, or Java. Here, you'll learn to construct robust server-side applications, manage data storage and retrieval, and implement authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Mastering Database Management:
A pivotal aspect of backend development is comprehending databases. You'll delve into relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as NoSQL databases like MongoDB. Proficiency in database management systems and design principles enables the creation of scalable and efficient applications.
Exploring Frontend Frameworks and Libraries:
In addition to backend development, you'll deepen your expertise in frontend technologies. You'll explore prominent frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, or Vue.js, streamlining the creation of interactive and responsive user interfaces.
Learning Version Control with Git:
Version control is indispensable for collaborative software development. During this phase, you'll familiarize yourself with Git, a distributed version control system, to manage your codebase, track changes, and collaborate effectively with fellow developers.
Achieving Mastery: Advanced Phase (2+ Years)
As you ascend in your journey, you'll enter the advanced phase of full stack development, where you'll refine your skills, tackle intricate challenges, and delve into specialized domains of interest.
Designing Scalable Systems:
In the advanced stage, focus shifts to designing scalable systems capable of managing substantial volumes of traffic and data. You'll explore design patterns, scalability methodologies, and cloud computing platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Embracing DevOps Practices:
DevOps practices play a pivotal role in contemporary software development. You'll delve into continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, infrastructure as code (IaC), and containerization technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes.
Specializing in Niche Areas:
With experience, you may opt to specialize in specific domains of full stack development, whether it's frontend or backend development, mobile app development, or DevOps. Specialization enables you to deepen your expertise and pursue career avenues aligned with your passions and strengths.
Conclusion:
Becoming a proficient full stack developer is a transformative journey that demands dedication, resilience, and perpetual learning. By following the roadmap outlined in this guide and maintaining a curious and adaptable mindset, you'll navigate the complexities and opportunities inherent in the realm of full stack development. Remember, mastery isn't merely about acquiring technical skills but also about fostering collaboration, embracing innovation, and contributing meaningfully to the ever-evolving landscape of technology.
#full stack developer#education#information#full stack web development#front end development#frameworks#web development#backend#full stack developer course#technology
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Key Programming Languages Every Ethical Hacker Should Know
In the realm of cybersecurity, ethical hacking stands as a critical line of defense against cyber threats. Ethical hackers use their skills to identify vulnerabilities and prevent malicious attacks. To be effective in this role, a strong foundation in programming is essential. Certain programming languages are particularly valuable for ethical hackers, enabling them to develop tools, scripts, and exploits. This blog post explores the most important programming languages for ethical hackers and how these skills are integrated into various training programs.
Python: The Versatile Tool
Python is often considered the go-to language for ethical hackers due to its versatility and ease of use. It offers a wide range of libraries and frameworks that simplify tasks like scripting, automation, and data analysis. Python’s readability and broad community support make it a popular choice for developing custom security tools and performing various hacking tasks. Many top Ethical Hacking Course institutes incorporate Python into their curriculum because it allows students to quickly grasp the basics and apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. In an Ethical Hacking Course, learning Python can significantly enhance your ability to automate tasks and write scripts for penetration testing. Its extensive libraries, such as Scapy for network analysis and Beautiful Soup for web scraping, can be crucial for ethical hacking projects.
JavaScript: The Web Scripting Language
JavaScript is indispensable for ethical hackers who focus on web security. It is the primary language used in web development and can be leveraged to understand and exploit vulnerabilities in web applications. By mastering JavaScript, ethical hackers can identify issues like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and develop techniques to mitigate such risks. An Ethical Hacking Course often covers JavaScript to help students comprehend how web applications work and how attackers can exploit JavaScript-based vulnerabilities. Understanding this language enables ethical hackers to perform more effective security assessments on websites and web applications.
Biggest Cyber Attacks in the World
youtube
C and C++: Low-Level Mastery
C and C++ are essential for ethical hackers who need to delve into low-level programming and system vulnerabilities. These languages are used to develop software and operating systems, making them crucial for understanding how exploits work at a fundamental level. Mastery of C and C++ can help ethical hackers identify and exploit buffer overflows, memory corruption, and other critical vulnerabilities. Courses at leading Ethical Hacking Course institutes frequently include C and C++ programming to provide a deep understanding of how software vulnerabilities can be exploited. Knowledge of these languages is often a prerequisite for advanced penetration testing and vulnerability analysis.
Bash Scripting: The Command-Line Interface
Bash scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks on Unix-based systems. It allows ethical hackers to write scripts that perform complex sequences of commands, making it easier to conduct security audits and manage multiple tasks efficiently. Bash scripting is particularly useful for creating custom tools and automating repetitive tasks during penetration testing. An Ethical Hacking Course that offers job assistance often emphasizes the importance of Bash scripting, as it is a fundamental skill for many security roles. Being proficient in Bash can streamline workflows and improve efficiency when working with Linux-based systems and tools.
SQL: Database Security Insights
Structured Query Language (SQL) is essential for ethical hackers who need to assess and secure databases. SQL injection is a common attack vector used to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications that interact with databases. By understanding SQL, ethical hackers can identify and prevent SQL injection attacks and assess the security of database systems. Incorporating SQL into an Ethical Hacking Course can provide students with a comprehensive understanding of database security and vulnerability management. This knowledge is crucial for performing thorough security assessments and ensuring robust protection against database-related attacks.
Understanding Course Content and Fees
When choosing an Ethical Hacking Course, it’s important to consider how well the program covers essential programming languages. Courses offered by top Ethical Hacking Course institutes should provide practical, hands-on training in Python, JavaScript, C/C++, Bash scripting, and SQL. Additionally, the course fee can vary depending on the institute and the comprehensiveness of the program. Investing in a high-quality course that covers these programming languages and offers practical experience can significantly enhance your skills and employability in the cybersecurity field.
Certification and Career Advancement
Obtaining an Ethical Hacking Course certification can validate your expertise and improve your career prospects. Certifications from reputable institutes often include components related to the programming languages discussed above. For instance, certifications may test your ability to write scripts in Python or perform SQL injection attacks. By securing an Ethical Hacking Course certification, you demonstrate your proficiency in essential programming languages and your readiness to tackle complex security challenges. Mastering the right programming languages is crucial for anyone pursuing a career in ethical hacking. Python, JavaScript, C/C++, Bash scripting, and SQL each play a unique role in the ethical hacking landscape, providing the tools and knowledge needed to identify and address security vulnerabilities. By choosing a top Ethical Hacking Course institute that covers these languages and investing in a course that offers practical training and job assistance, you can position yourself for success in this dynamic field. With the right skills and certification, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle the evolving challenges of cybersecurity and contribute to protecting critical digital assets.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
My Recommended Pathway to Learning Code
Why Learn to Code?
Unleash Creativity: Coding is like painting with words. You get to create digital masterpieces, bring ideas to life, and build things you've always imagined.
Problem-Solving Superpower: Ever felt the satisfaction of solving a puzzle? Coding is a series of problem-solving adventures where you're the hero armed with logic and creativity.
Endless Possibilities: From websites to apps, games, and beyond, coding opens doors to endless possibilities. Imagine the impact you can make in the digital realm!
Where to Begin?
Starting your coding journey can be overwhelming, and I don't blame you for thinking so. Begin with these beginner-friendly languages:
HTML/CSS: The dynamic duo for web development. HTML structures content, while CSS styles it. Perfect for creating your first website. Think of HTML as the structure for a building. The frame, if you will. CSS will be the decor of it all.
JavaScript: The language of the web. It adds interactivity to your sites, making them dynamic and engaging.
Python: A versatile language, loved for its readability. Great for beginners and used in various fields, from web development to data science.
The Importance of Learning Foundations:
Think of coding as building a house. You wouldn't start with the roof, right? Learning foundational languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is like laying a strong foundation. Here's why it matters:
Understanding the Basics: Foundations teach you the core concepts of programming, helping you understand how code works.
Transferable Skills: The skills you gain are transferable to other languages. Once you grasp the logic, moving on becomes a smoother journey. You can't read a book if you don't know the alphabet.
Confidence Booster: Starting with the basics builds confidence. It's like leveling up in a game – you become more adept and ready for the next challenge.
Problem-Solving Mindset: Foundations instill a problem-solving mindset. As you conquer challenges, you develop a resilient approach to coding conundrums.
Starting up:
I highly recommend using what you have on hand. Notepad on Windows works great but if you'd like something more code based try out:
Notepad++
Sublime
Visual Code Studio
Coffee Cup
Atom (This has been sunset though, so use at your own risk)
Any questions? Please feel free to message me! I might take 24 hours to respond, but I will get back to you!
#CodingJourney#HTML#CSS#JavaScript#Python#WebDevelopment#learn#pathway#recommendation#cs#computer#science#compsci#programming#edu#educational#codeblr#studyblr
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's understand HTML

Cover these topics to complete your HTML journey.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used to create web pages. Here's a comprehensive list of key topics in HTML:
1. Basics of HTML
Introduction to HTML
HTML Document Structure
HTML Tags and Elements
HTML Attributes
HTML Comments
HTML Doctype
2. HTML Text Formatting
Headings (<h1> to <h6>)
Paragraphs (<p>)
Line Breaks (<br>)
Horizontal Lines (<hr>)
Bold Text (<b>, <strong>)
Italic Text (<i>, <em>)
Underlined Text (<u>)
Superscript (<sup>) and Subscript (<sub>)
3. HTML Links
Hyperlinks (<a>)
Target Attribute
Creating Email Links
4. HTML Lists
Ordered Lists (<ol>)
Unordered Lists (<ul>)
Description Lists (<dl>)
Nesting Lists
5. HTML Tables
Table (<table>)
Table Rows (<tr>)
Table Data (<td>)
Table Headings (<th>)
Table Caption (<caption>)
Merging Cells (rowspan, colspan)
Table Borders and Styling
6. HTML Forms
Form (<form>)
Input Types (<input>)
Text Fields (<input type="text">)
Password Fields (<input type="password">)
Radio Buttons (<input type="radio">)
Checkboxes (<input type="checkbox">)
Drop-down Lists (<select>)
Textarea (<textarea>)
Buttons (<button>, <input type="submit">)
Labels (<label>)
Form Action and Method Attributes
7. HTML Media
Images (<img>)
Image Maps
Audio (<audio>)
Video (<video>)
Embedding Media (<embed>)
Object Element (<object>)
Iframes (<iframe>)
8. HTML Semantic Elements
Header (<header>)
Footer (<footer>)
Article (<article>)
Section (<section>)
Aside (<aside>)
Nav (<nav>)
Main (<main>)
Figure (<figure>), Figcaption (<figcaption>)
9. HTML5 New Elements
Canvas (<canvas>)
SVG (<svg>)
Data Attributes
Output Element (<output>)
Progress (<progress>)
Meter (<meter>)
Details (<details>)
Summary (<summary>)
10. HTML Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
Canvas
Inline SVG
Path Element
11. HTML APIs
Geolocation API
Drag and Drop API
Web Storage API (localStorage and sessionStorage)
Web Workers
History API
12. HTML Entities
Character Entities
Symbol Entities
13. HTML Meta Information
Meta Tags (<meta>)
Setting Character Set (<meta charset="UTF-8">)
Responsive Web Design Meta Tag
SEO-related Meta Tags
14. HTML Best Practices
Accessibility (ARIA roles and attributes)
Semantic HTML
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) Basics
Mobile-Friendly HTML
15. HTML Integration with CSS and JavaScript
Linking CSS (<link>, <style>)
Adding JavaScript (<script>)
Inline CSS and JavaScript
External CSS and JavaScript Files
16. Advanced HTML Concepts
HTML Templates (<template>)
Custom Data Attributes (data-*)
HTML Imports (Deprecated in favor of JavaScript modules)
Web Components
These topics cover the breadth of HTML and will give you a strong foundation for web development.
Full course link for free: https://shorturl.at/igVyr
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thoughts on Web Programming
The basic approach to web programming is through structure (HTML), description of structure (CSS), and action (Javascript).
Javascript modifies webpage structure, and structural description.
My interest with web programming is in the production of dynamic and uniquely user configurable websites, with an emphasis on background data display (a stats for nerds page).
Maybe this is like the developer console.
And perhaps, any approach to actually *teaching* web programming should orient itself around correct usage of the browser developer console.
Writing a website has been challenging, for awhile. But understanding this tool is key to understanding the actual broader structure of the internet, on the client side.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Codetober day 17:
So I'm working on my game again.
So I'm switching out the architecture of my game to an Entity Component System, and I was using a library called Pico Ecs which is an stb style single header library.
But after using it for literally a morning there were inconsistencies and bugs popping up. And I've programmed enough to see where this is going.
So I started work on my own ecs, which in c can be done with some function pointers and the right data structure.
Which in this case is a Sparse Set, which I'm still wrapping my brain around. But all I know is that data is stored in a densely packed array, and the indices for the data you want is stored in a sparsely packed array.
Also you are limited to arrays, no linked lists or anything. And there are only a handful of instances a sparse data set can be used for do to its strict typing.
But the positive with sparse sets is, adding, deleting, and SEARCHING are all O(1) time. Which means no matter how many items are in the dataset it takes the same ammount of time to access it.
Basically its perfect for entity component systems.
I wanna make a video breaking it down once I finish it so stay tuned.
17. What's a programming/tech thing you feel very strongly about?
The decision to use Javascript to build applications is the single worst idea to ever be thought in computer science. Even worse than OOP.
I used to think "oh I dont know javascript super well maybe it's not so bad". After learning javascript inside and out, it is truly the most poorly designed piece of shit language to ever be created. It seems to challenge itself to come up with the most abstract absurd solutions to problems that could be solved with a single function. If the guy tasked with making the language spent a little more than 10 days designing it we as a sphere of engineering would have saved millions of hours of programming hours and billions of dollars in wasted cpu cycles.
Javascript is fine for powering buttons and login forms. But the fact that Visual Studio Code is written in Javascript is such a bafflingly stupid decision I'm unsure if the words exist to describe it.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
java full stack
A Java Full Stack Developer is proficient in both front-end and back-end development, using Java for server-side (backend) programming. Here's a comprehensive guide to becoming a Java Full Stack Developer:
1. Core Java
Fundamentals: Object-Oriented Programming, Data Types, Variables, Arrays, Operators, Control Statements.
Advanced Topics: Exception Handling, Collections Framework, Streams, Lambda Expressions, Multithreading.
2. Front-End Development
HTML: Structure of web pages, Semantic HTML.
CSS: Styling, Flexbox, Grid, Responsive Design.
JavaScript: ES6+, DOM Manipulation, Fetch API, Event Handling.
Frameworks/Libraries:
React: Components, State, Props, Hooks, Context API, Router.
Angular: Modules, Components, Services, Directives, Dependency Injection.
Vue.js: Directives, Components, Vue Router, Vuex for state management.
3. Back-End Development
Java Frameworks:
Spring: Core, Boot, MVC, Data JPA, Security, Rest.
Hibernate: ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework.
Building REST APIs: Using Spring Boot to build scalable and maintainable REST APIs.
4. Database Management
SQL Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL (CRUD operations, Joins, Indexing).
NoSQL Databases: MongoDB (CRUD operations, Aggregation).
5. Version Control/Git
Basic Git commands: clone, pull, push, commit, branch, merge.
Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket.
6. Build Tools
Maven: Dependency management, Project building.
Gradle: Advanced build tool with Groovy-based DSL.
7. Testing
Unit Testing: JUnit, Mockito.
Integration Testing: Using Spring Test.
8. DevOps (Optional but beneficial)
Containerization: Docker (Creating, managing containers).
CI/CD: Jenkins, GitHub Actions.
Cloud Services: AWS, Azure (Basics of deployment).
9. Soft Skills
Problem-Solving: Algorithms and Data Structures.
Communication: Working in teams, Agile/Scrum methodologies.
Project Management: Basic understanding of managing projects and tasks.
Learning Path
Start with Core Java: Master the basics before moving to advanced concepts.
Learn Front-End Basics: HTML, CSS, JavaScript.
Move to Frameworks: Choose one front-end framework (React/Angular/Vue.js).
Back-End Development: Dive into Spring and Hibernate.
Database Knowledge: Learn both SQL and NoSQL databases.
Version Control: Get comfortable with Git.
Testing and DevOps: Understand the basics of testing and deployment.
Resources
Books:
Effective Java by Joshua Bloch.
Java: The Complete Reference by Herbert Schildt.
Head First Java by Kathy Sierra & Bert Bates.
Online Courses:
Coursera, Udemy, Pluralsight (Java, Spring, React/Angular/Vue.js).
FreeCodeCamp, Codecademy (HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
Documentation:
Official documentation for Java, Spring, React, Angular, and Vue.js.
Community and Practice
GitHub: Explore open-source projects.
Stack Overflow: Participate in discussions and problem-solving.
Coding Challenges: LeetCode, HackerRank, CodeWars for practice.
By mastering these areas, you'll be well-equipped to handle the diverse responsibilities of a Java Full Stack Developer.
visit https://www.izeoninnovative.com/izeon/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Zillow Scraping Mastery: Advanced Techniques Revealed

In the ever-evolving landscape of data acquisition, Zillow stands tall as a treasure trove of valuable real estate information. From property prices to market trends, Zillow's extensive database holds a wealth of insights for investors, analysts, and researchers alike. However, accessing this data at scale requires more than just a basic understanding of web scraping techniques. It demands mastery of advanced methods tailored specifically for Zillow's unique structure and policies. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of Zillow scraping, unveiling advanced techniques to empower data enthusiasts in their quest for valuable insights.
Understanding the Zillow Scraper Landscape
Before diving into advanced techniques, it's crucial to grasp the landscape of zillow scraper. As a leading real estate marketplace, Zillow is equipped with robust anti-scraping measures to protect its data and ensure fair usage. These measures include rate limiting, CAPTCHA challenges, and dynamic page rendering, making traditional scraping approaches ineffective. To navigate this landscape successfully, aspiring scrapers must employ sophisticated strategies tailored to bypass these obstacles seamlessly.
Advanced Techniques Unveiled
User-Agent Rotation: One of the most effective ways to evade detection is by rotating User-Agent strings. Zillow's anti-scraping mechanisms often target commonly used User-Agent identifiers associated with popular scraping libraries. By rotating through a diverse pool of User-Agent strings mimicking legitimate browser traffic, scrapers can significantly reduce the risk of detection and maintain uninterrupted data access.
IP Rotation and Proxies: Zillow closely monitors IP addresses to identify and block suspicious scraping activities. To counter this, employing a robust proxy rotation system becomes indispensable. By routing requests through a pool of diverse IP addresses, scrapers can distribute traffic evenly and mitigate the risk of IP bans. Additionally, utilizing residential proxies offers the added advantage of mimicking genuine user behavior, further enhancing scraping stealth.
Session Persistence: Zillow employs session-based authentication to track user interactions and identify potential scrapers. Implementing session persistence techniques, such as maintaining persistent cookies and managing session tokens, allows scrapers to simulate continuous user engagement. By emulating authentic browsing patterns, scrapers can evade detection more effectively and ensure prolonged data access.
JavaScript Rendering: Zillow's dynamic web pages rely heavily on client-side JavaScript to render content dynamically. Traditional scraping approaches often fail to capture dynamically generated data, leading to incomplete or inaccurate results. Leveraging headless browser automation frameworks, such as Selenium or Puppeteer, enables scrapers to execute JavaScript code dynamically and extract fully rendered content accurately. This advanced technique ensures comprehensive data coverage across Zillow's dynamic pages, empowering scrapers with unparalleled insights.
Data Parsing and Extraction: Once data is retrieved from Zillow's servers, efficient parsing and extraction techniques are essential to transform raw HTML content into structured data formats. Utilizing robust parsing libraries, such as BeautifulSoup or Scrapy, facilitates seamless extraction of relevant information from complex web page structures. Advanced XPath or CSS selectors further streamline the extraction process, enabling scrapers to target specific elements with precision and extract valuable insights efficiently.
Ethical Considerations and Compliance
While advanced scraping techniques offer unparalleled access to valuable data, it's essential to uphold ethical standards and comply with Zillow's terms of service. Scrapers must exercise restraint and avoid overloading Zillow's servers with excessive requests, as this may disrupt service for genuine users and violate platform policies. Additionally, respecting robots.txt directives and adhering to rate limits demonstrates integrity and fosters a sustainable scraping ecosystem beneficial to all stakeholders.
Conclusion
In the realm of data acquisition, mastering advanced scraping techniques is paramount for unlocking the full potential of platforms like Zillow. By employing sophisticated strategies tailored to bypass anti-scraping measures seamlessly, data enthusiasts can harness the wealth of insights hidden within Zillow's vast repository of real estate data. However, it's imperative to approach scraping ethically and responsibly, ensuring compliance with platform policies and fostering a mutually beneficial scraping ecosystem. With these advanced techniques at their disposal, aspiring scrapers can embark on a journey of exploration and discovery, unraveling valuable insights to inform strategic decisions and drive innovation in the real estate industry.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Computer Language
Computer languages, also known as programming languages, are formal languages used to communicate instructions to a computer. These instructions are written in a syntax that computers can understand and execute. There are numerous programming languages, each with its own syntax, semantics, and purpose. Here are some of the main types of programming languages:
1.Low-Level Languages:
Machine Language: This is the lowest level of programming language, consisting of binary code (0s and 1s) that directly corresponds to instructions executed by the computer's hardware. It is specific to the computer's architecture.
Assembly Language: Assembly language uses mnemonic codes to represent machine instructions. It is a human-readable form of machine language and closely tied to the computer's hardware architecture
2.High-Level Languages:
Procedural Languages: Procedural languages, such as C, Pascal, and BASIC, focus on defining sequences of steps or procedures to perform tasks. They use constructs like loops, conditionals, and subroutines.
Object-Oriented Languages: Object-oriented languages, like Java, C++, and Python, organize code around objects, which are instances of classes containing data and methods. They emphasize concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
Functional Languages: Functional languages, such as Haskell, Lisp, and Erlang, treat computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions. They emphasize immutable data and higher-order functions.
Scripting Languages: Scripting languages, like JavaScript, PHP, and Ruby, are designed for automating tasks, building web applications, and gluing together different software components. They typically have dynamic typing and are interpreted rather than compiled.
Domain-Specific Languages (DSLs): DSLs are specialized languages tailored to a specific domain or problem space. Examples include SQL for database querying, HTML/CSS for web development, and MATLAB for numerical computation.
3.Other Types:
Markup Languages: Markup languages, such as HTML, XML, and Markdown, are used to annotate text with formatting instructions. They are not programming languages in the traditional sense but are essential for structuring and presenting data.
Query Languages: Query languages, like SQL (Structured Query Language), are used to interact with databases by retrieving, manipulating, and managing data.
Constraint Programming Languages: Constraint programming languages, such as Prolog, focus on specifying constraints and relationships among variables to solve combinatorial optimization problems.
2 notes
·
View notes